Citrus inodora UN-2024b Assembly & Annotation
Overview
| Analysis Name | Citrus inodora UN-2024b Assembly & Annotation |
| Sequencing technology | PacBio Sequel |
| Assembly method | hifiasm v. v.0.19.8 |
| Release Date | 2024-12-17 |
Nakandala U, Furtado A, Masouleh AK, Smith MW, Mason P, Williams DC, Henry RJ. The genomes of Australian wild limes. Plant Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 24;114(5):102. doi: 10.1007/s11103-024-01502-4.
AbstractAustralian wild limes occur in highly diverse range of environments and are a unique genetic resource within the genus Citrus. Here we compare the haplotype-resolved genome assemblies of six Australian native limes, including four new assemblies generated using PacBio HiFi and Hi-C sequencing data. The size of the genomes was between 315 and 391 Mb with contig N50s from 29.5 to 35 Mb. Gene completeness of the assemblies was estimated to be from 98.4 to 99.3% and the annotations from 97.7 to 98.9% based upon BUSCO, confirming the high contiguity and completeness of the assembled genomes. High collinearity was observed among the genomes and the two haplotype assemblies for each species. Gene duplication and evolutionary analysis demonstrated that the Australian citrus have undergone only one ancient whole-genome triplication event during evolution. The highest number of species-specific and expanded gene families were found in C. glauca and they were primarily enriched in purine, thiamine metabolism, amino acids and aromatic amino acids metabolism which might help C. glauca to mitigate drought, salinity, and pathogen attacks in the drier environments in which this species is found. Unique genes related to terpene biosynthesis, glutathione metabolism, and toll-like receptors in C. australasica, and starch and sucrose metabolism genes in both C. australis and C. australasica might be important candidate genes for HLB tolerance in these species. Expanded gene families were not lineage specific, however, a greater number of genes related to plant-pathogen interactions, predominantly disease resistant protein, was found in C. australasica and C. australis.
Assembly statistics
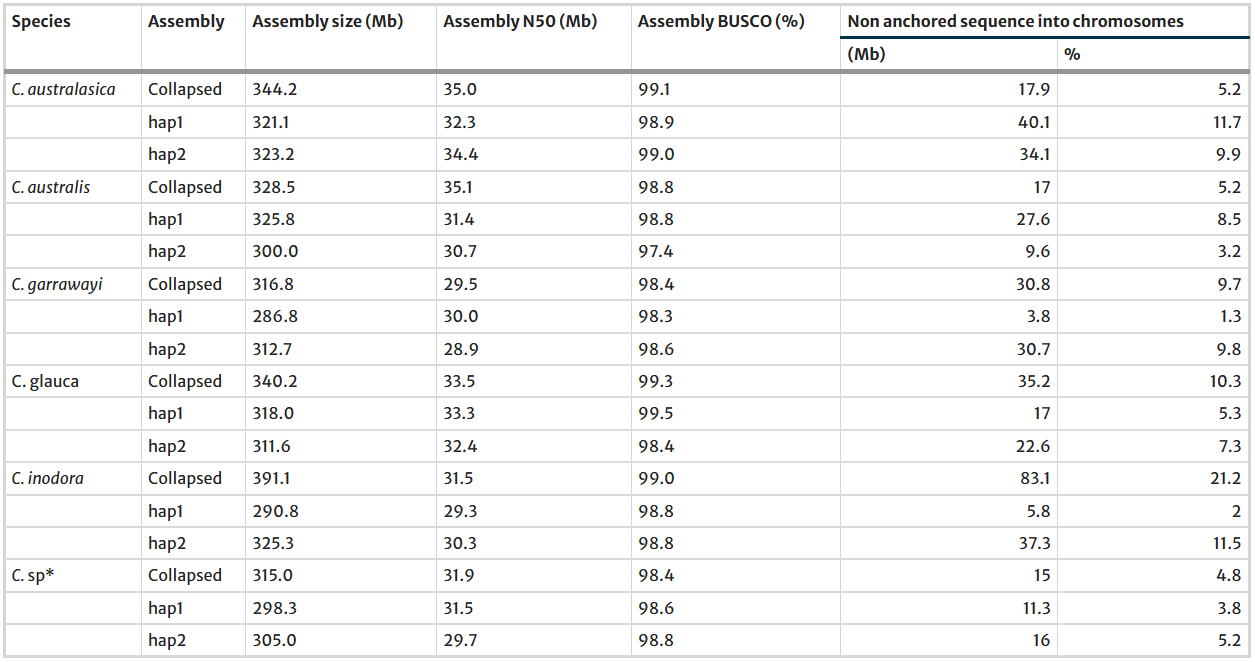
Assembly
The Citrus inodora UN-2024b Assembly files are available in FASTA format.
Downloads
| Chromosomes (FASTA file) | GCA_046118865.1_ASM4611886v1_genomic.fna.gz |
| Chromosomes (FASTA file) | GCA_046118875.1_ASM4611887v1_genomic.fna.gz |
Gene Predictions
The Citrus inodora UN-2024b genome gene prediction files are not available.
Downloads
| Genes (GFF3 file) | - |
| CDS sequences (FASTA file) | - |
| Protein sequences (FASTA file) | - |
Functional Analysis
Functional annotation for the Citrus inodora UN-2024b is not available.
Downloads
| Domain from InterProScan | - |
S genes
Summary
| Query | Chr | Size(bp) | Coordinates | BLASTn Hit | BLASTn %ID | Domain |
| SLF1 | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27556835-27557935 | PP719840.1, S30-SLF1 | 97 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF2a | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27559914-27561038 | PP719841.1, S30-SLF2 | 97 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF3 | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27565889-27567010 | PP719842.1, S30-SLF3 | 95 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF4 | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27570708-27571823 | PP719843.1, S30-SLF4 | 91 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF5 | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27589031-27587904 | PP719830.1, S2-SLF5 | 86 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF2b | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27601981-27600869 | PP719841.1, S30-SLF2 | 88 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF9aψ | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27626562-27627700 | PP719834.1, S2-SLF9 | 74 | - |
| SLF7 | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27629874-27628744 | PP719832.1, S2-SLF7 | 92 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF8 | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27632488-27633630 | PP719847.1, S30-SLF8a | 75 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF9b | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27636328-27637467 | PP719834.1, S2-SLF9 | 74 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF10 | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27657970-27659115 | PP719835.1, S2-SLF10 | 99 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF11ψ | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27661554-27660384 | PP719851.1, S30-SLF11 | 98 | - |
| SLF12 | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27667242-27666121 | PP719837.1, S2-SLF12 | 99 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| S-RNase | CM100387.1 | 28733469 | 27574785-27574543,27574449-27573997 | MN652903.1, S7-RNase | 98 | RNase T2 |
| SLF1 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26580397-26581497 | PP719840.1, S30-SLF1 | 97 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF7 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26684648-26683518 | PP719832.1, S2-SLF7 | 92 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF8 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26687262-26688404 | PP719847.1, S30-SLF8a | 75 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF9 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26691219-26692358 | PP719834.1, S2-SLF9 | 74 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF10 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26712855-26714000 | PP719835.1, S2-SLF10 | 99 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF11ψ | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26716443-26715269 | PP719851.1, S30-SLF11 | 98 | - |
| SLF12 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26720594-26719473 | PP719837.1, S2-SLF12 | 99 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF2 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26583485-26584609 | PP719841.1, S30-SLF2 | 94 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF3 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26592374-26593495 | PP719842.1, S30-SLF3 | 91 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF4 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26619294-26620409 | PP719843.1, S30-SLF4 | 90 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF5 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26661252-26660128 | PP719830.1, S2-SLF5 | 88 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
| SLF6 | CM100396.1 | 28277361 | 26673712-26672588 | PP719845.1, S30-SLF6 | 91 | F-box; F_box_assoc |
Citrus inodora UN-2024b S genes Nucleotide
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF1 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF2a mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF3 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF4 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF5 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF2b mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF9aψ mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF7 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF8 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF9b mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF10 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF11ψ mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF12 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 S-RNase mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF1 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF7 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF8 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF9 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF10 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF11ψ mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF12 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF2 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF3 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF4 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF5 mRNA, complete cds
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF6 mRNA, complete cds
Citrus inodora UN-2024b S genes Protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF1 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF2a protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF3 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF4 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF5 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF2b protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF7 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF8 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF9b protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF10 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 SLF12 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap1 S-RNase protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF1 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF7 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF8 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF9 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF10 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF12 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF2 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF3 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF4 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF5 protein
- Citrus inodora UN-2024b hap2 SLF6 protein